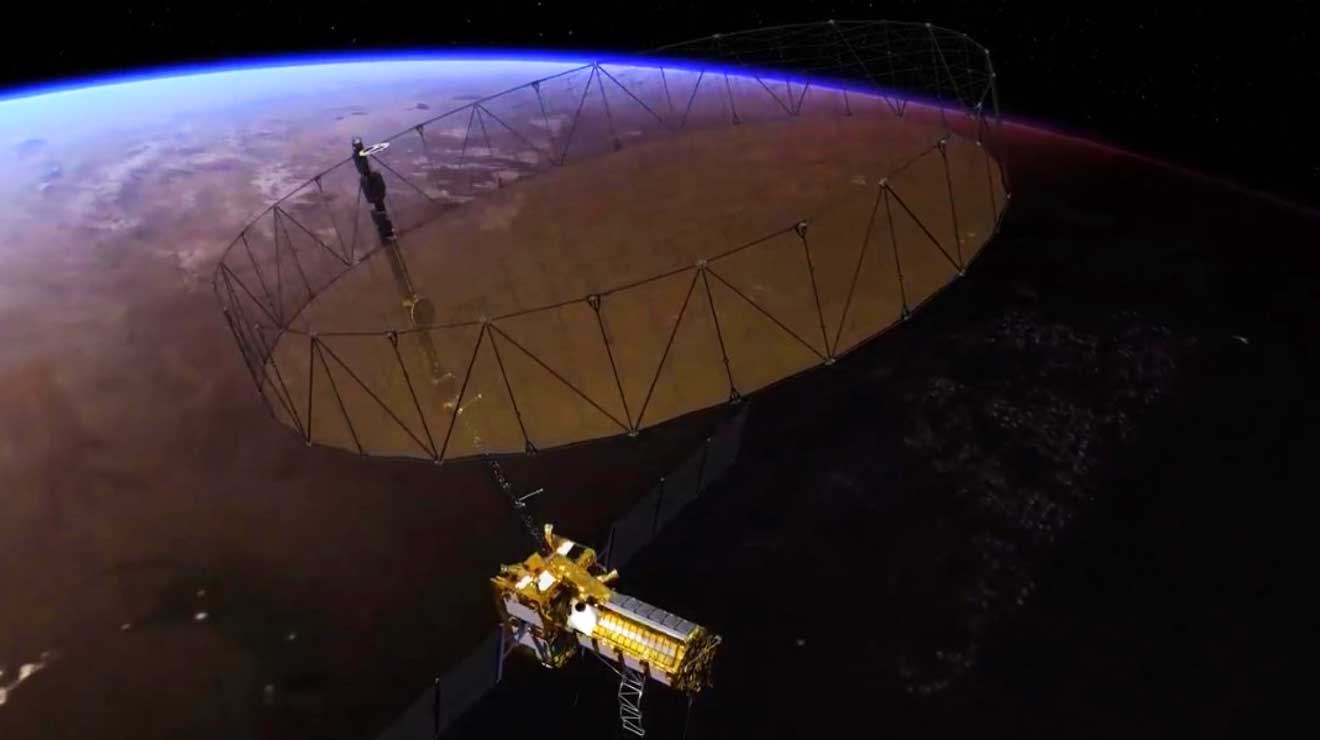
NASA and ISRO are currently working on the development of NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar), which is a visionary satellite that will detect the surface motions of the Earth.
The satellite will be launched into a near-polar orbit in 2022 from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota in India. It will scan the globe every twelve days for three years, mapping the Earth’s land, ice sheets, and sea ice.
This satellite will be the first to utilise multiple frequencies for radar imaging. It will be used for remote sensing, which will allow scientists to watch and comprehend natural processes on Earth. Its left-facing equipment, for example, will explore the Antarctic cryosphere. NISAR is expected to be the most costly Earth-imaging satellite in the world, with a cost of $1.5 billion.
NISAR will survey the height of Earth’s land and ice masses four to six times per month at resolutions of five to ten metres using enhanced radar imaging. It is intended to watch and quantify some of the most complex natural processes on the globe, such as ecological disruptions, ice-sheet collapse, and natural disasters including earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides.
So with this mission, ISRO as well as NASA have high hopes.

















Add Comment